Analog vs. Digital Trigger
- 11 Dec 2020
I don’t think anyone would be willing to debate the importance of an oscilloscope’s trigger system. The abilities to look at a stable display and capture specific events are absolutely essential. In a nutshell, the trigger system is responsible for recognizing a user-specified event, stopping signal acquisition, and positioning the acquired signal on the display. And while this capability has been around for a long time, a new approach has some key advantages.
In the 5 Series MSO, with its new ASIC, our engineers implemented a digital trigger system instead of the more traditional analog trigger. Why? What are some of the advantages?
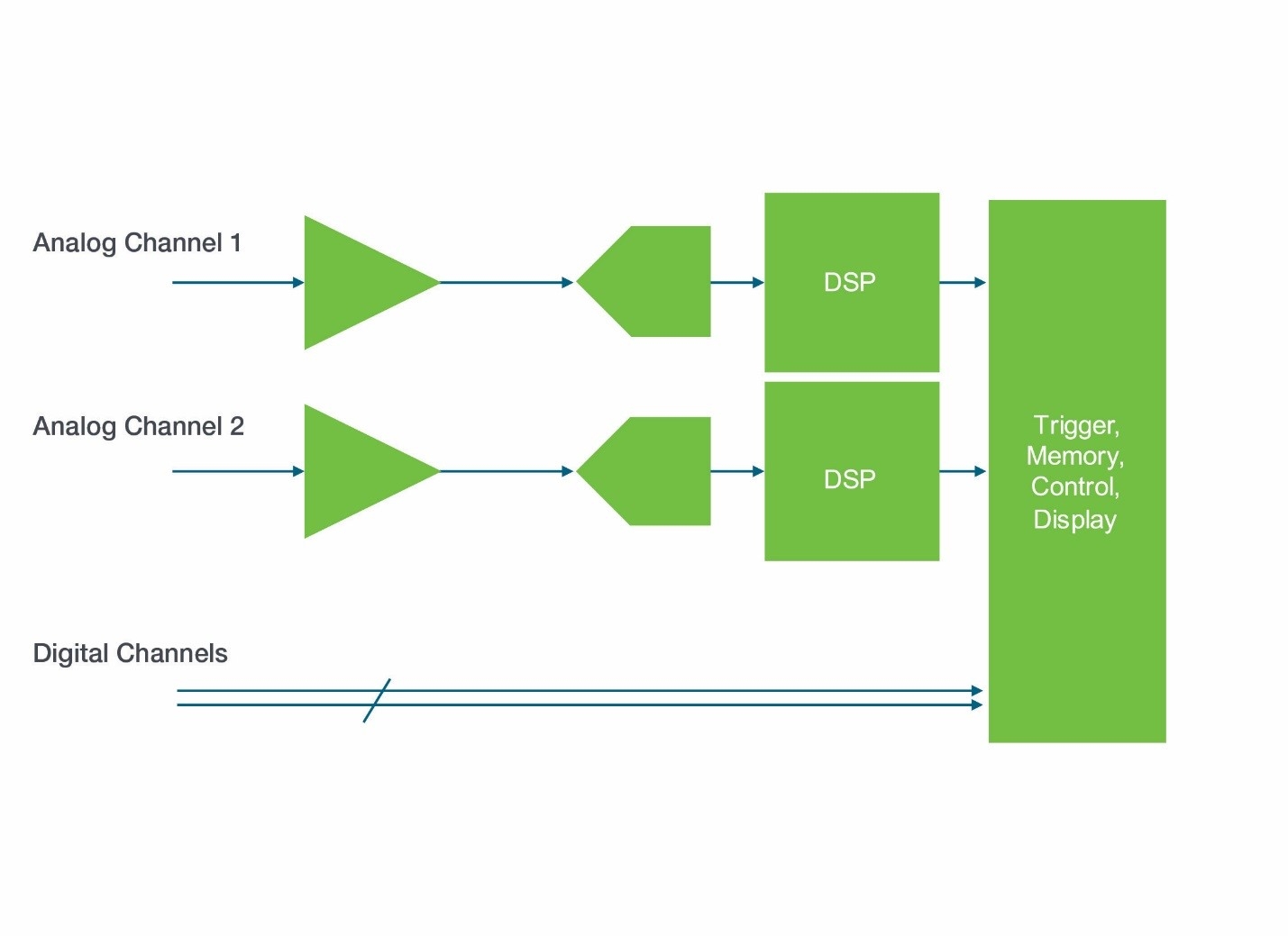
Traditionally, the trigger circuit was based on analog or mixed-signal processing of analog input signals. Though these trigger input signals were similar to the signals digitized by the ADCs, they traveled through the instrument by separate paths, possibly encountering different gains, offsets, coupling, bandwidths, distortions, and noise levels. Scope engineers put huge effort into making sure these paths perform the same, but in an analog trigger design, the fact remains that there are multiple paths.
Traditional oscilloscope trigger system with separate analog signal input paths
The trigger design in the 5 Series isn’t the first digital trigger in a Tek scope. In the early 2000s, Tektronix introduced digital triggering with the MSO/DPO2000 Series. These oscilloscopes used the same digitized signal to drive the trigger ASIC and the rest of the acquisition system, assuring high performance at low cost.
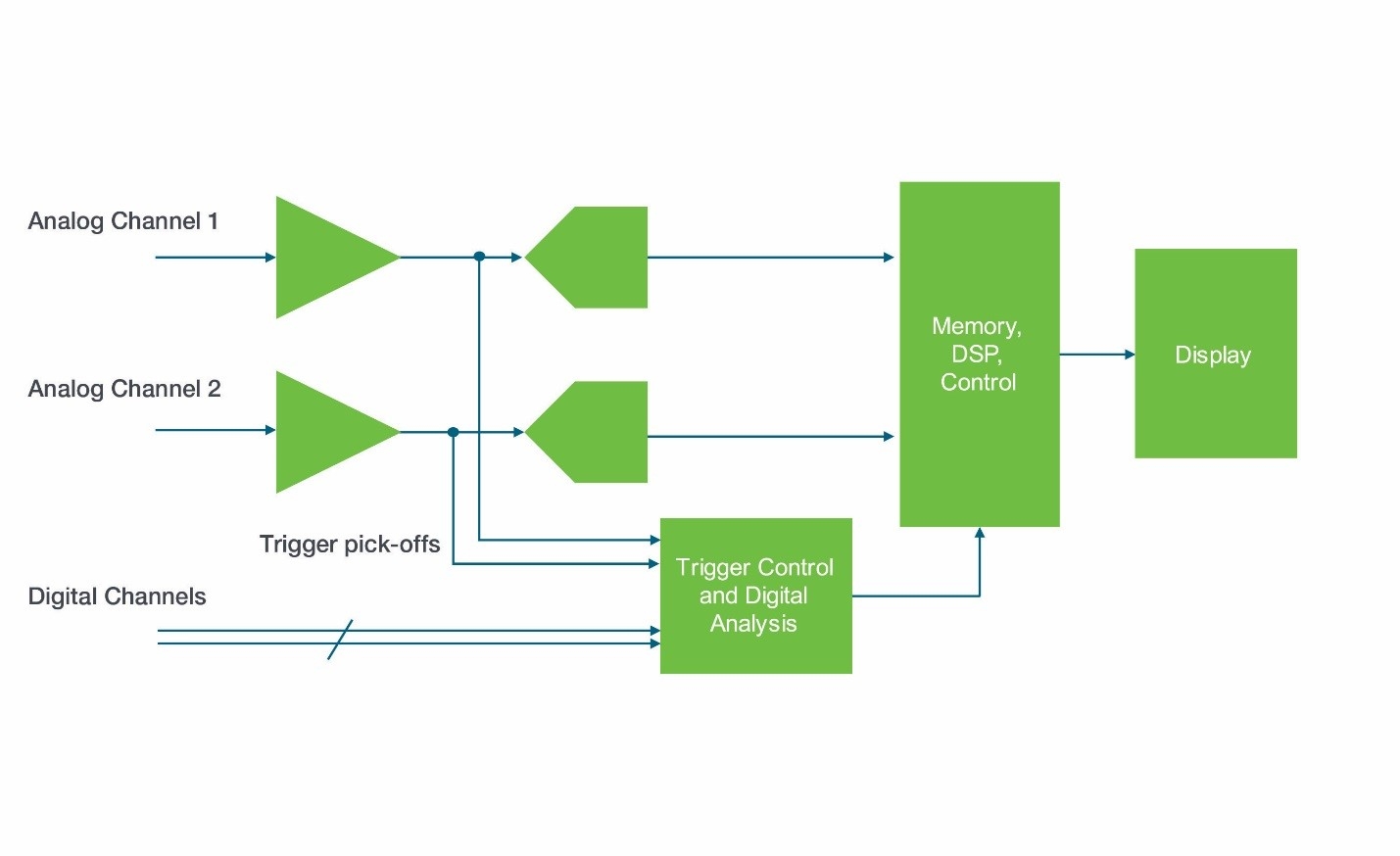
The 5 Series MSO hardware provides the next-generation digital trigger, with much higher real-time performance. Because the trigger system uses the same signal path as the acquisition system, any signal conditioning in the acquisition path (coupling, bandwidth limiting, deskew, and High Res acquisition processing) also affects the trigger signal, giving the user new levels of adjustment and confidence.
Digital oscilloscope trigger system using acquired digitized input signals
The 5 Series MSO’s digital trigger provides another significant measurement capability – the 8-digit trigger frequency counter. (It is available for free, along with the optional digital voltmeter. just for registering the oscilloscope on tek.com.) This frequency counter provides a readout of the trigger event frequency (e.g. edge, pulse width, runt, or serial or parallel bus pattern) up to about a 150 MHz rate with 1 Hz resolution.
The idea of a digital trigger system might be new, and bring with it some anxiety for those of us with a strong analog affinity. But when such a design is executed well, it offers better alignment between the trigger and acquisition systems. Single-signal path, digital triggering is one of the ways the 5 Series MSO has improved performance. Take a look at the datasheet to learn more.