The Leakage Current Measurement of Capacitors with GW Instek PSU Series Power Supply
- 11 Dec 2020
Capacitor’s leakage current is generally expressed by insulation resistance, which is one of important parameters for capacitor. Before measuring capacitor’s leakage current, the capacitor must be fully charged and the test voltage must be stabilized. Capacitor, a circuit component, contains two metallic plates separated by a dielectric medium. An electric current flowing through a capacitor comprises three current components including the charging current from test voltage to the capacitor and the equivalent branch current RεCεfrom dialectic.
The current value of the equivalent branch current is inverse proportional to Rε. The branch current will attenuate to zero ampere by the time index. The last one is leakage current flowing through insulation resistance Rp. Since these three current components will change over time, the measurement of leakage current must be taken under the criteria of a fully charged capacitor and a stabilized branch current Rε Cε, which is close to zero ampere as shown on the following diagrams:
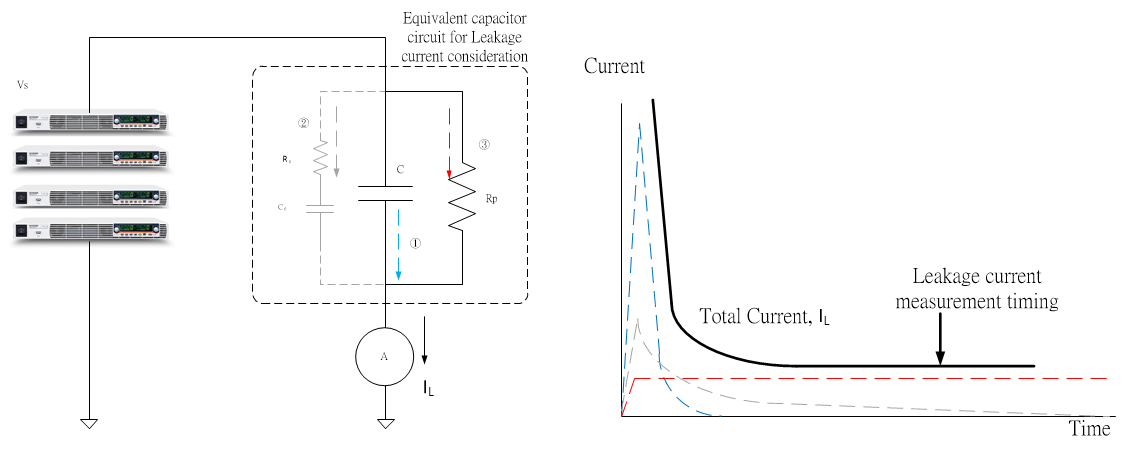
Capacitor’s leakage current measurement is often carried out by ATE consisting of the PSU series due to that the series provides comprehensive communications interfaces including LAN, RS-232, RS-485, USB and analog control interface to benefit users in integrating ATE and editing user-defined test procedures. The GW Instek PSU series provides a large output of 1.5KW by its 1U height and19” unit rack, which can flexibly augment voltage and current output capacities so as to satisfy capacitor’s different test requirements by parallel and series connections.
The CC priority function of the series provides CC mode at the very beginning of the operation to prevent peak current occurred at crossover between CV and CC from damaging capacitor that is different from other power supplies, which must convert CV to CC. Adjustable slew rate allows users based upon requirements to adjust rise time for voltage or current to verify capacitive characteristics.
Note:
The amount of branch current from dielectric is determined by the characteristics of dielectric materials. Under most circumstances, branch current from dielectric materials is very small and it can be neglected.
Find out more about the GW Instek PSU Series >




